FINENESS OF CEMENT
LABORATORY TEST
(FINENESS OF CEMENT BY DRY SIEVING ) : AS per IS:4031-part1-1996
The laboratory test are conducted based on the standards published by the Indian standard. The quality of cement is found by conducting the fines of cement. Which is conducted at certain conditions.This test is performed unless otherwise having the temperature of 27+ or - 20C and 65+ or - 5% of relative humidity of the laboratory.
The humidity influences the fines of
cement test (IS: 269 – 1976 and IS: 4031 – 1968). Increase in the humidity percentage then the formation of
lumps will increase. Due to the lump formation residue
percentage in the sieve will
increase. Finally which effects the test results.
Apparatus required:
1.
Balance of accuracy 0.01 g
2.
IS sieve of 90 microns
Procedure:
1.
Break down any air – set lumps in
the cement sample by using a clean dry rod
2.
Weigh accurately 100 g of the cement
and place it on a standard 90 micron IS sieve with the pan below to collect the
sieved cement.
3.
Sieve the sample continuously for 15
minutes.
4.
Weigh the residue left on the sieve.
Calculation
1.
Weight of the residue on the sieve
after sieving: ______ g
2.
Fineness =
Discussion:
1.
The fineness percentage should not
exceed 10 for OPC and 5% for RHC.
2.
Higher the fineness percentage, poorer the
quality of the cement.
3.
Fineness of cement has a great
effect on the rate of hydration and hence the rate of obtaining the strength of
concrete.
4.
Fineness of cement increases the
rate of evolution of heat.
5.
Finer cement offers a great surface
area for hydration and hence faster the
development of strength.
6.
Increase in fineness of cement also
increases the drying shrinkage of concrete and hence creates cracks in
structures.
7.
Excessive fineness requirement
increases cost of grinding.
8.
Excessive fine cement requires more
water for hydration, resulting reduced
strength and durability.
9.
Fineness of cement affects
properties like gypsum requirement, workability
of fresh concrete & long term behavior of structure.
10.
Coarse cement particles settle down
in concrete which causes bleeding.
Precaution
- Air set lumps of cement should be broken by using a clean dry rod before sieving the sample
- Sieving should be done by rotating the sieve and but not by translation.



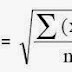
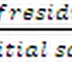





nice explanation fineness of cement
ReplyDelete