EARTHQUAKE RESISTANT DESIGN
EARTHQUAKE RESISTANT DESIGN
HI GOOD MORNING TO DAY WE CAME WITH A TECHNIQUES OF EARTHQUAKE RESISTANCE DESIGN
Now a day’s earthquake is a major problem regarding the
damage of lives and also majorly economy. Economy means damage to structures of
civil engineering .to reduces the damage we need to protect the building from
earth quake and we need to make the building as earth quake proof. Here comes
the details of earth quake resistant design from the beginning of the
definitions for the persons who even don`t know about any earth quake
terminology
Let`s learn my loving visitors
Earthquakes are
a major geological phenomena. Man has been terrified of this phenomena for
ages, as little has been known about the causes of earthquakes, but it leaves
behind a trail of destruction. There are hundreds of small earthquakes around
the world everyday. Some of them are so minor that humans cannot feel them, but
seismographs and other sensitive machines can record them. Earthquakes occur
when tectonic plates move and rub against each other. Sometimes, due to this
movement, they snap and rebound to their original position. This might cause a
large earthquakes as the tectonic plates try to settle down. This is known as
the Elastic Rebound Theory.
Every year, earthquakes
take the lives of thousands of people , and destroy property worth billions.
The 2010 Haiti Earthquake killed over 1,50,000 people and destroyed entire
cities and villages. Designing Earthquake Resistant Structures is
indispensable. It is imperative that structures are designed to resist
earthquake forces, in order to reduce the loss of life. The science of
Earthquake Engineering and Structural Design has improved tremendously, and
thus, today, we can design safe structures which can safely withstand
earthquakes of reasonable magnitude.
Natural Calamities
Natural
calamities are the phenomenon which can’t be prevented, but we can take
precautions to minimize their effects. Calamities such as Floods, Cyclones,
Volcanic eruptions, Tsunamis and Earthquakes can cause a lot of damage to life
and property, and cause disturbance to our day-to-day life.
What is an Earthquake?
An earthquake is
a sudden, rapid shaking of the Earth caused by the breaking and shifting of
rock beneath the Earth’s surface. For hundreds of millions of years, the forces
of plate tectonics have shaped the Earth as the huge plates that form the
Earth’s surface move slowly over, under, and past each other. Sometimes the
movement is gradual. At other times, the plates are locked together, unable to
release the accumulating energy. When the accumulated energy grows strong
enough, the plates break free causing the ground to shake. Most earthquakes
occur at the boundaries where the plates meet; however, some earthquakes occur
in the middle of plates.
Ground shaking
from earthquakes can collapse buildings and bridges; disrupt gas, electric, and
phone services; and sometimes trigger landslides, avalanches, flash floods,
fires, and huge, destructive ocean waves (tsunamis). Buildings with foundations
resting on unconsolidated landfill and other unstable soil, and trailers and
homes not tied to their foundations are at risk because they can be shaken off
their mountings during an earthquake. When an earthquake occurs in a populated
area, it may cause deaths and injuries and extensive property damage.
Hence the
saying,
“Earthquake
don’t kill people, buildings do.”
The dynamic
response of building to earthquake ground motion is the most important cause of
earthquake-induced damage to buildings. The damage that a building suffers
primarily depends not upon its displacement, but upon acceleration. Whereas
displacement is the actual distance the ground and building may move during an
earthquake, acceleration is a measure of how quickly they change speed as they
move. The conventional approach to earthquake resistant design of buildings
depends upon providing the building with strength, stiffness and inelastic
deformation capacity which are great to withstand a given level of earthquake-generated
force. This is generally accomplished through
the selection of
an appropriate structural configuration and the carefully detailing of
structural members, such as beams and columns, and the connections between
them.
In contrast, we
can say that the basic approach underlying more advanced techniques for
earthquake resistance is not to strength the building, but to reduce the
earthquake-generated forces acting upon it. By de-coupling the structure from
seismic ground motion it is possible to reduce the earthquake-induced forces in
it. This can be done in a number of ways. Some popular techniques are
Increase natural
period of structure by “Base Isolation Techniques”.Increase damping of the
system by “Energy Dissipation Devices”.
u can download this stuff through Google
u can download this stuff through Google


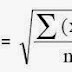





0 comments :