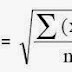DIFFERENCE BETWEEN 43 Grade & 53 Grade
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN 43 Grade & 53 Grade
OPC 43 Grade Cement
OPC 43 grade cement is (Conforming to IS: 8122-1989) a cheaper comparative to OPC 53 grade cement. OPC 43 grade cement also has fine grinding of clinkers but comparatively less than OPC 53. This causes it to have a slower gain in strength when compared with 53grade and also the comparative lack of magnesium by a difference of -0.01%. This percentage of magnesium content affects the heat of hydration performance. Due to this the 43grade cement gains the strength slower.
Advantages of 43grade cement:
Due to the low heat of hydration comparative to 53grade. it develops less cracks
no need to take extra precautions while laying concrete slabs.
by using this we can reduce the leeching effects.
- it is less cost comparative to 53grade
Disadvantages of 43grade cement:
it gains strength slower comparative to 53grade. due to this de-shattering of form work will take more time comparative to 53grade


OPC 53 Grade Cement
OPC 53 grade cement is (Conforming to IS:12269-1967) the most preferred building material for construction of projects where require high tensile strength. As 53 grade cement has the grinding of clinkers to the maximum extent and this cement grade is finer than grade 43.
The
fineness in cement generates early gain in strength, but along with
high heat of hydration. however, is further
supported in by magnesium strength which is 6.01% in OPC 53, only 0.01%
higher than that in OPC 43. These differences cause a difference in
potential phase composition of clinker which affects the final
compressive strength.
The heat of hydration in the 53grade cement is very high which triggers reaction to get maximum strength in less time compare to the 43 grade. Because of this advantage the 53grade cement is most preferred building material in the construction industry. which enables the early de-shattering the form work in the construction projects
Advantages of 53grade cement:
Due to the Quick heat of hydration it gains maximum strength in less time than 43grade.
work progress will be more in construction sites. because it reduce the De-shattering time in site
Disadvantages of 53grade cement:
- Need to take extra precautions while laying concrete slabs.
- by using this we can reduce the leeching effects.
- it is slightly more cost comparative to 43grade